deque adt
Dequeues support add and remove operations from either end of the data, rather than a specialized place like Stacks and Queues.
What is a Deque?
- Deque - a "double-ended queue"
- Does not mean that it is searchable
- Does not have a single expected removal behavior compared to Stacks or Queues
- Can add or remove from both sides
Deque model:

Deque supported operations
void addFirst(x)- Add to the first indexvoid addLast(x)- Add to the last indexx removeFirst()- Remove from the first indexx removeLast()- Remove from the last indexboolean isEmpty()- Check if the Deque is emptyint size()- Return the size
Deque unsupported operations
- Searching for data
- Arbitrary index access
- Arbitrary adding/removing at indexes
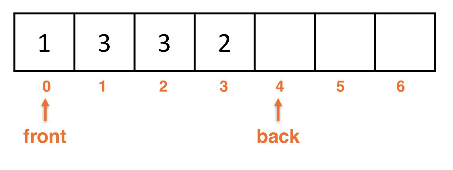
Array backed Deques
- Use a circular, wrap-around array implementation
Array backed methods
addLast()- increment back (mod by capcacity)- Add to back
removeLast()- remove at back -> decrement back- (check if < 0) because we can't go to -1 to wrap around the front
- If we're in the negative we have to set the marker (
frontorback) we set this to thesize
- If we're in the negative we have to set the marker (
- the
%(mod) behaves differently with negative numbers in java
- (check if < 0) because we can't go to -1 to wrap around the front
- Implementation would be in O(1) for these operations
- Add and remove would be amortized O(1)* due to the resizing that may occur
Array backed Deque:
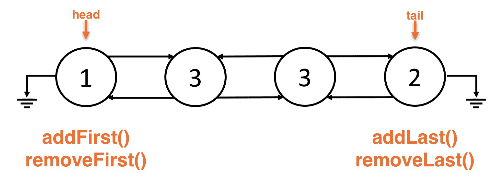
Linked list backed Deques
- We use a doubly linked list because singly would be very inefficient
addFirst()andremoveFirst()are both done at theheadaddLast()andremoveLast()are both done at thetail
Linked list Deque:
Linkedlist backed methods
addFirst()- add to theheadaddLast()- add to thetailremoveFirst()- remove from theheadremoveLast()- remove from thetail- All of these operations have O(1) time complexity
Examples
- Online purchasing systems
- Enqueue to the front during purchasing
- Dequeue when the purchase completes
- Customer can enqueue to the front of the deck again if they need to make changes to their purchase