linked structures
Circularly linked lists are a small change to general linkedlists. These can be flexible in a large number of ways.
Example, each node "receives" one pointer but can have outgoing pointers:
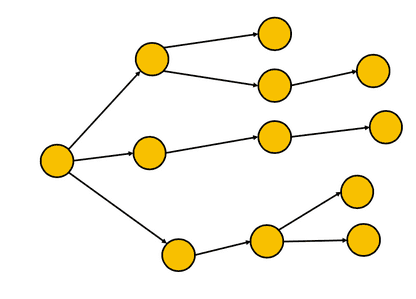
Tree structures
These are very common structures, one example is a file system.
Reversing the previous example says we can have multiple pointers being received by 1 pointer:
- This is similar to a folder structure
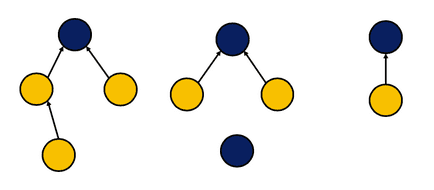
Disjoint set
Disjoint set system is a grouping where every sequence of node connections lead to a single, unique node (blue nodes). These are a "representative" for a grouping of nodes.
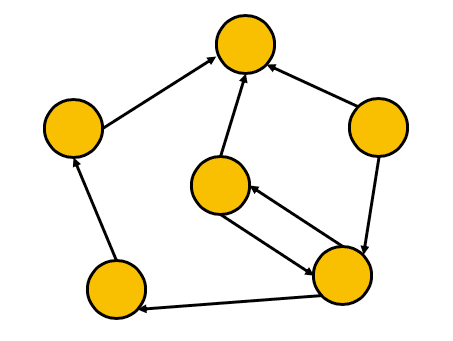
Graph structures
This graph structure is a linkedlist with no restrictions on the number of pointers in or out of a node.
These are used to model relationships between data and are generally a flexible concept. This is used quite a bit in social networks where nodes represent people and connections are certain properties that are shared.