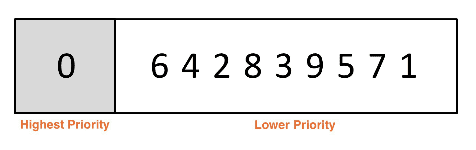priority queues
Priority queues are similar to stacks and queues because they are linear.
The expected behavior is different than a regular queue.
Priority queue ADT
- Stack ADT:
- Remove -> Most recently added element
- Queue ADT:
- Remove -> Least recently added element
- Priority Queue ADT:
- Remove -> Element with the highest priority
Priority Queue diagram:
Common uses
-
Retrieve minimum values from a collection of data
-
Retrieve maximum values of a data set
-
Because there is a priority element the data is typically comparable
- This allows us to distinguish between high and low priority elements
Priority Queue example:
Priority queue implementations
Problem is efficiently ranking by priority.
Solution is utilizing heaps to solve the priority problem.
Example use cases
- Waiting room in an emergency room
- Boarding a plane based on ticket class - first, business, coach
- In graph algorithms, minimum spanning trees. Finding the shortest path from A to B
Priority Queues as a linear model?
This doesn't make sense much for a Priority Queue because we would be pulling from different points along the queue. We want to maintain a sorted list, either with an array-backed sorted list or a linked sorted list.
Array-backed would be similar to an ArrayQueue where the highest priority would be at the front of the list, while the lowest priority is at the back.
- Dequeueing and peek would be O(1)
- Enqueueing would be O(n), even with amortized resizing
- We have to maintain the sorted order by shifting data around to place things
LinkedQueue implementation where the head is the highest priority and tail is lowest.
- Peeking and dequeueing would be O(1)
- Enqueueing would be O(n) because we have to find the location to insert data