binary search tree (bst)
A type of binary tree with the same properties but enforce a data order property.
Properties
A binary search tree enforces order:
- The left child data is less than the parent data
- The parent data is less than the right child's data
- All of the data on the left sub tree must be less than the data in the parent node
- All data in the right sub tree must be more than the node
Example of a valid BST:

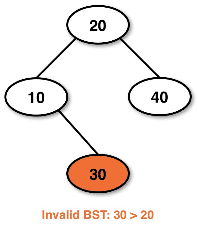
Invalid BST example:
Implementing and efficiency of BSTs
- In Java the data in a BST must implement the
Comparableinterface- This must have the
compareTomethod
- This must have the
- Motivation for binary search
- Each comparison tells you the data is to the left or the right
- We have to search half the data, rather than all of it
- This is an O(logn) runtime
- Performance depends on the shape of the tree
- Time complexity for a degenerate tree (aka a linkedlist) is O(n)
Traversals
Traversals are categorized into two groups, depth and breadth searches.
Depth traversals (stack based)
Depth searches travel down the tree, like going down a rabbit hole. These follow a path or branch as deep as it can go until it reaches a null child.
Examples:
- Preorder traversal
- Inorder traversal
- Postorder traversal
Breadth traversal (queue based)
Breadth searches travel one level at a time, these explore one step away from the root, then two steps away, etc.
Example:
- Levelorder traversal