tree structures
Trees are a gateway concept toward efficient search procedures.
Previous structures
- All previous list-based ADTs are not efficient for searching
- When looking at a linkedlist or arraylist we have to traverse in O(n)
- Similarly, Deques, Queues, and Stacks are limited in their operations
Tree ADT
- Conceptually, a tree is a linked structure where each node has a parent-child relationship
- Linkedlists are technically trees, just simple ones
- A node has a single parent but can have multiple children
- Trees - connected linked structures with no cycles
- A cycle would be like a circularly linked list, where you can loop to the head
- Can be implemented in a variety of ways, depending on the details of the type of tree
- Most commonly we use linkedlist structures with
Nodesandpointers
- Most commonly we use linkedlist structures with
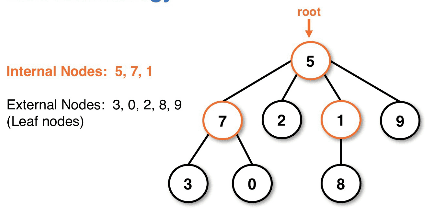
Tree diagram example:

Root of the tree:
Terminology
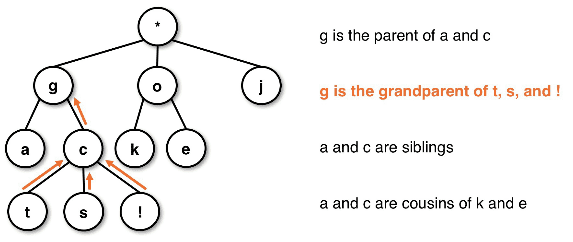
- root - the top node (a node with no parents)
- internal node (parent) - a node with children
- external node (leaf) - a node with no children
- cousin nodes are of the same "generation" but with different parent nodes
- relative position is the depth that the node resides at, this is used to classify
Tree root relationship diagram:
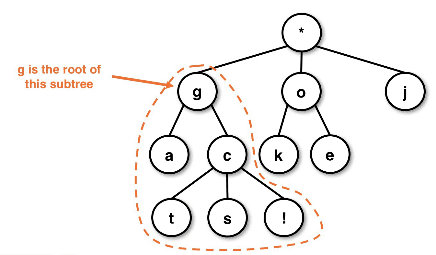
Subtrees are children of the root node:
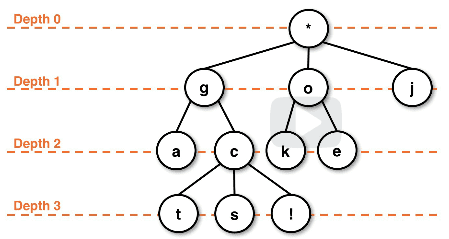
Node depth for relative position classification:
General concepts
- Think of each of the child nodes under the root as their own sub tree
- This is important to remember during the recursive operations used to traverse
- Valid subtrees can be
nullor even single, one-elemnt node trees - Relative positions within the hierarchy care used as both a classification and reference
- Depth refers to the distance from the
rootnode - The height of any leaf node is always
0and is generally easiest from the leafs up- This would be a bottom-up approach
Height(node) = (Max. child height) + 1Height(leaf) = 0
- Depth refers to the distance from the
- Operations for the tree ADT are similar to other structures
addandremovemethods- Query methods like
getandcontains - Accessor methods like
sizeandisEmpty
- There is no concept of front and back like in linear models
Properties
- Shape - What is the structure of the nodes in the tree?
- Structure of the tree
- Order - How is the data arranged in the tree?
- How the data is arranged inside the structure
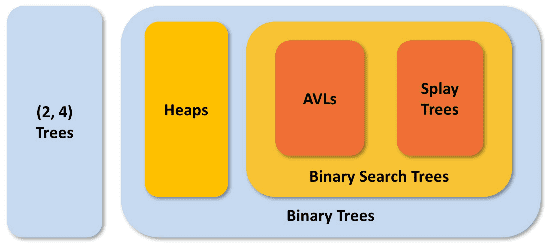
Classification of trees
- Trees can be either a data structure or ADT depending on the language
- Below are groupings of tree types
Tree structure classifications: