aws elastic load balancers
Load balancers distribute network traffic across a group of servers. This routes traffic to different webservers based on things like, round robin or based on which server is the least busy.
If a single webserver fails, the load balancer will not send requests to it until it comes online.
Additionally, we can add more webservers as traffic increases and the load balancer can have them registered then route traffic to it.
Types of load balancers
- Application load balancer - http/https
- Network load balancer - TCP and high performance
- Classic load balancer (legacy) - http/https and TCP
- Gateway load balancer - balances workloads for 3rd party virtual appliances running AWS
- Virtual applicances on the AWS marketplace
- Virtual firewals like Fortinet, Palto Alto
Application load balancer
This balances HTTP/HTTPs traffic. These operate at layer 7 (application) of the OSI model, which makes it application aware.
- Supports advanced request routing to specific web servers based on the HTTP header
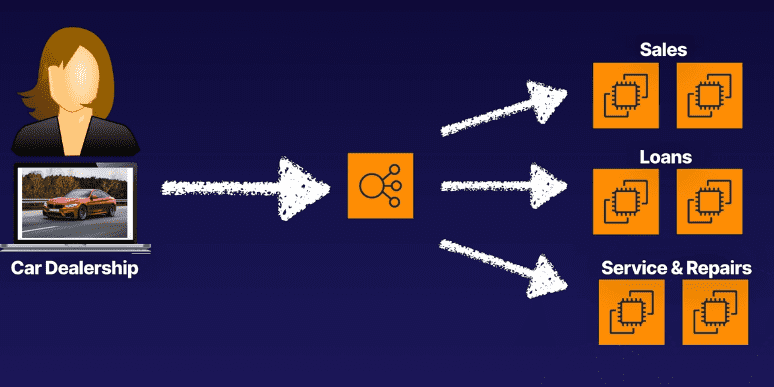
Example of an application-level load balancer to route to web servers:
Network load balancer
A high performance option for TCP traffic, where extreme performance is needed. Operates at the layer 4 transport later.
- Handles millions of requests per second with low latency
Classic load balancer (legacy)
Supports some layer 7 specific features (X-Forwarded-For) headers and sticky sessions.
Handles layer 4 load balancing for TCP protocol.
X-Forwarded-For header
Allows a service to identify the originating IP address of a client connecting through a load balancer. This enables the application to keep sessions alive while passing through the load balancer.
Common load balancer errors
Most comon is the Error 504 Gateway timeout. This means that the target server downstream
has failed to respond.
General troubleshooting
- Check that the application is alive
- Determine if the target connection is having issues
- Check where the app specifically is failing to determine if there are issues with
the connectivity
Exam tips
- App load balancers routes to web servers based on request types (http/https)
- Network load balancer for high performance (TCP traffic)
- Classic load balancer (http/https/TCP)
- Gateway load balancer for 3rd party appliances
- X-Forwarded-For header to enable sticky sessions