aws codedeploy features
CodeDeploy offers CICD in various ways, these were covered in a previous note that had an overview of the different code hosting solutions that AWS offers.
More nitty gritty features
- In-place deployment:
- capacity is reduced during the deployment
- Lambda is not supported
- Rolling back involves a re-deploy
- Great when deploying the first time
- Blue/Green deployment:
- No capacity reduction (safest option)
- Green instances can be created ahead of time
- Easy to switch between old and new
- You pay for 2 environments until you terminate the old servers
CodeDeploy AppSpec file
AppSpecfile - Configuration file for the parameters to be used during the CodeDeploy
deployment
- For EC2 and on-premises systems the file is YAML only
- For Lambda YAML and JSON are supported
EC2 AppSpec file structure
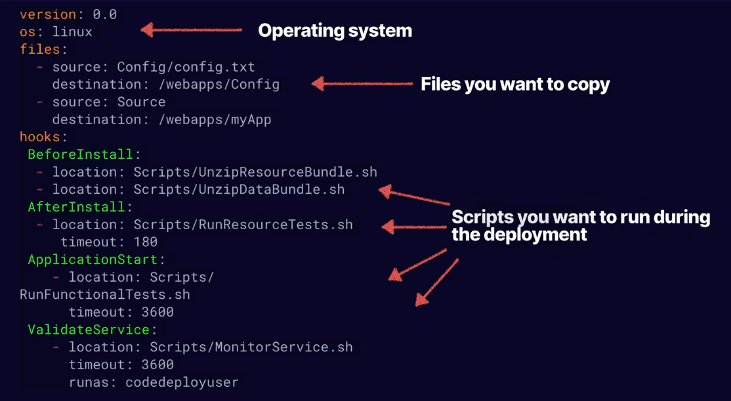
- version - reserved for future use (0.0 is only value now)
- OS - operating system version you're using (linux, windows, etc.)
- files - config files, packages, locations of where files are and should be copied to
- hooks - lifecycle event hooks, aka scripts that need to run during the deployment
lifecycle. Hooks have a specific run order
Example scripts during a deployment:
- Unzip application files
- Run tests on a newly deployed application
- Deal with load balancing - de-register and re-register instances with a load balancer
Example EC2 appspec.yml:
Typical folder structure for CodeDeploy is:
- appspec.yml
- /Scripts
- /Config
- /Source
Note: The appspec.yml file needs to be in the root directory
AppSpec lifecycle event hooks
Lifecycle event hooks happen in 3 phases during a deployment.
- Phase 1:
- De-register instances from a load balancer
- Phase 2:
- Nuts and bolts of the application deployment
- Phase 3:
- Re-register instances with the load balancer
Phase 1
The following are in order of execution for lifecycle event hooks before deployment:
- BeforeBlockTraffic:
- Tasks that youw ant to run on instances before they are deregistered from
- BlockTraffic:
- Block - de-register instances from a load balancer
- AfterBlockTraffic:
- Tasks you want to run on instances after they are de-registered from a load
Phase 2
Run order for an in-place deployment:
- ApplicationStop - gracefully stop the application
- DownloadBundle - CodeDeploy agent copies application files to a temp location
- BeforeInstall - pre-installation scripts, like backing up a current version, decrypting files
- Install - copy application revision files to final location
- AfterInstall - post-install scripts like configuration, file permissions, etc.
- ApplicationStart - start any services that were stopped during ApplicationStop
- Could be a script or set of commands to run
- ValidateService - run tests to validate the service
Phase 3
The following hooks are run after the app is installed:
- BeforeAllowTraffic - tasks to run on instances before they're registered with the
load balancer
- AllowTraffic - register instances with the load balancer
- AfterAllowTraffic - things to run after registering with the load balancer