aws elastic container service intro
Containers are similar to a virtual machine, more like a virtual operating environment.
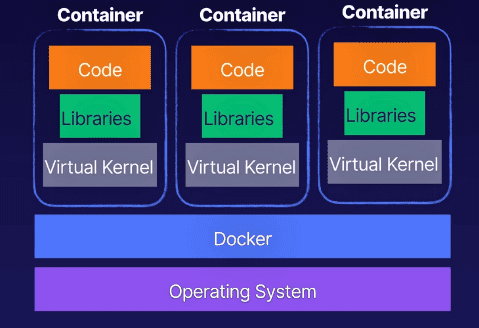
- Standardized - These are standardized units with everything the software needs to run (libraries,
system tools, code, etc.).
- Microservices - applications are created using independent, stateless components
or microservices running in containers * These are typically stateless and can be started/stopped/scaled independently * AWS has a whitepaper called "Running Microservices on AWS"
- Docker or windows containers - use Docker for any non-windows loads, Windows containers
for any Windows loads
Container architecture:
Advantages of containers & microservices architectures
- Highly scalable - if the application becomes over loaded, scale only the services you need to
- Fault tolerant - a single error in 1 of your containers won't bring down the whole app
- Easy to maintain - easier to maintain, update, and change than large mono-apps
What about ECS?
Container orchestration service that supports Docker and Windows containers.
This is similar to Kubernetes at a high level, but iwth deep integration with AWS services like IAM, VPC, Route53.
Quickly deploy and scale containerized workloads without having to install, configure, and manage/scale your own orchestration platform.
- Clusters of Virtual machines - ECS will run your containers on clusters of virtual machines
- EC2 instances have a lot more control
- Fargate for serverless - use Fargate for serverless containers to not worry about
the underlying EC2 instances
Elastic Container Registry
- Registry of container images for ECS to connect to and deploy Docker containers
Services using ECS
- Amazon Sagemaker - quickly deploy and scale ML models for training
- Amazon Lex - build conversational interfaces
- Amazon's own recommendation engine is runnong on ECS