launching an ec2 instance
These are some general notes from launching an EC2 instance. This demo from acloudguru.com has us configuring an EC2 instance as a web server.
General notes
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI) - The software configuration (OS, application server, and apps)
required to launch the instance.
- These images might be preconfigured for things like machine learning or databases
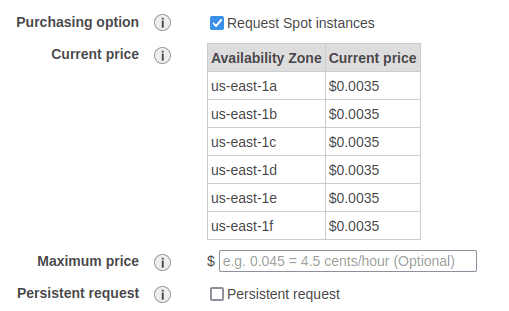
- Spot instances are at different price tiers and availability zones, but have reduced cost
Example spot instance pricing:
Startup scripts
- The user data section of the "advanced details" on EC2 creation allows for bootstrap scripts
- These are scripts/commands we want run when the instance is started
- Example: Update our operating system packages on startup
Storage volumes
- For storage we can choose to add new volumes and file systems for our EC2 instance
- Storage can be encrypted using KMS (key manage service) and it is very easy to manage
Tagging instances
- Tags are a way to organize instances with key-value pairs for naming, team ownership, or apps
Security
- Security groups are the firewalls that we have for our EC2. This is for access control
- By default we have SSH on port 22
- Adding a new HTTP rule for port 80 with a source of "anywhere" is what a webserver would need
- IPV4 notation:
0.0.0.0/0 - IPV6 notation:
::/0
- IPV4 notation:
SSH into the EC2
- On creation we have to create a key pair, and are given a
.pemfile- This needs to be stored in a secure location and shared sparingly
- Keys need to have their permissions set, using
chmod 400 <key name>
Changing our permissions of the .pem file:
chmod 400 <key name>.pem
To SSH into our server:
ssh ec2-user@<public IP> -i <key name>.pem
# continue?
> yes
Updating the EC2
We can do this as root, or as our ec2-user.
# -y for "yes"
yum update -y
Starting an Apache webserver at boottime
Creating an Apache webserver instance on startup of the EC2 instance will turn this into a tiny webserver.
# install Apache webserver
yum install httpd -y
# starts service
systemctl start httpd
# enable the service on startup
systemctl enable httpd
# check the status
systemctl status httpd